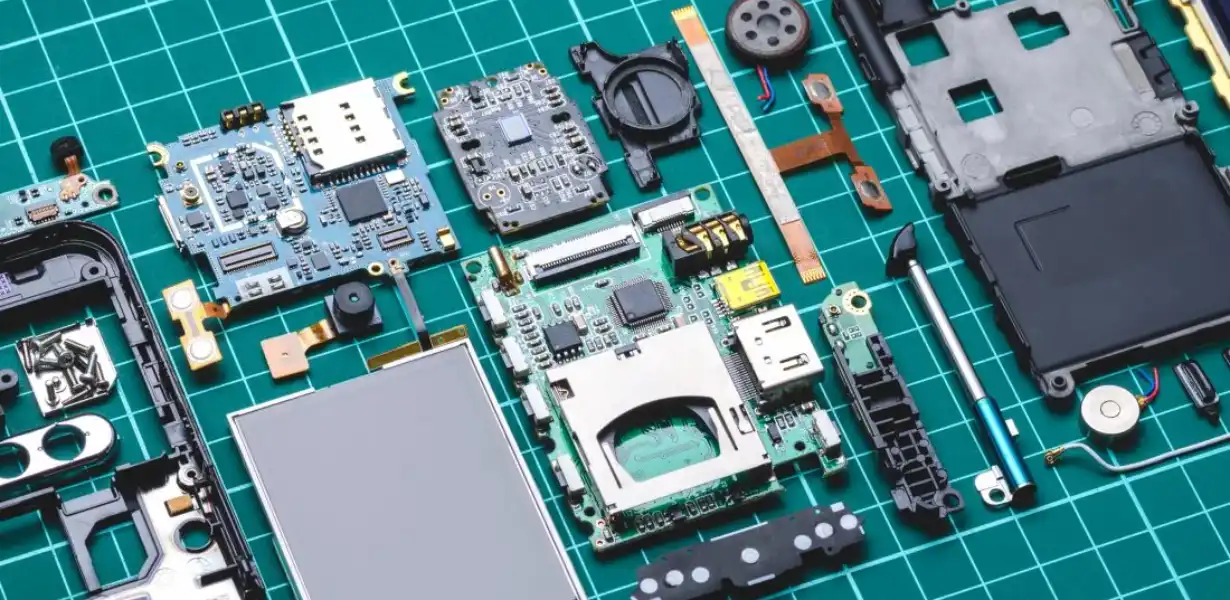
In the landscape of modern technology, the concept of sustainability in electronics is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for a more eco-friendly and ethical future. Our comprehensive exploration delves into the various facets of sustainable practices within the electronics industry, emphasizing the significance of this pivotal movement.
Understanding Sustainability in Electronics
Sustainability in electronics refers to the responsible production, use, and disposal of electronic devices to minimize their environmental impact. From the extraction of raw materials to the disposal of obsolete gadgets, every phase has implications for the environment and human health.
The Environmental Impact of Electronics Production
The production phase involves the extraction of raw materials, which often leads to environmental degradation. For instance, mining for minerals like coltan or cobalt, essential for electronic components, contributes to deforestation and hazardous working conditions.
Challenges in Design and Manufacturing
Incorporating eco-friendly designs and materials poses significant challenges for manufacturers. Creating durable products that can be easily repaired, upgraded, or recycled without compromising performance is crucial for sustainable electronics.
The Role of E-Waste in Environmental Sustainability
E-waste, the fastest-growing waste stream globally, poses a significant challenge. Recycling and proper disposal methods are imperative to reduce the environmental impact of discarded electronics. However, only a fraction of e-waste is appropriately recycled.
Energy Efficiency and Electronics
Energy efficiency plays a critical role in sustainability. Advancements in technology have allowed for more energy-efficient electronics, reducing their carbon footprint and operational costs.
Regulatory Framework and Ethical Considerations
Governments and international bodies are implementing regulations to address e-waste management and ensure ethical sourcing of materials. Compliance with these regulations is essential for a more sustainable electronics industry.
Innovations Driving Sustainability
Advancements in Material Science
Innovative materials like bioplastics, recycled metals, and bio-based components are revolutionizing electronics, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional materials.
Circular Economy Practices
The adoption of circular economy principles, where products are reused, repaired, or recycled, is gaining momentum in the electronics industry. Companies are increasingly embracing these practices to reduce waste and conserve resources.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
EPR programs hold manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, from production to disposal. This incentivizes companies to design more sustainable products and manage e-waste effectively.
Balancing Consumer Demand and Sustainability
Consumers play a pivotal role in driving sustainable change in the electronics industry. Educating and empowering them to make informed, eco-conscious choices can significantly impact the demand for sustainable electronics.
Consumer Awareness and Sustainable Choices
Empowering consumers with information on the environmental impact of their electronic devices encourages more conscious purchasing decisions, ultimately influencing manufacturers to produce greener products.
The Role of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Companies are increasingly integrating sustainability into their CSR initiatives, reflecting a commitment to social and environmental responsibility. This move towards sustainability resonates with consumers and enhances brand value.
The Path Ahead: A Call to Action
Sustainability in electronics is not an isolated effort but a collective responsibility of manufacturers, consumers, and policymakers. The transition to a more sustainable electronics industry requires collaborative efforts, innovative technologies, and informed decisions.
Final Words
Our journey through the realm of sustainability in electronics reveals both challenges and promising solutions. Embracing sustainable practices isn’t just a choice; it’s an imperative step towards a healthier planet and a more ethical industry. The road ahead demands continual innovation, awareness, and unified commitment.
Commonly Asked Questions
1. How can consumers contribute to sustainable electronics?
Consumers can make a difference by choosing products with eco-labels, supporting brands with sustainable practices, and properly recycling their old electronics.
2. What role do regulations play in promoting sustainability in electronics?
Regulations set standards for e-waste management, ethical sourcing, and energy efficiency, compelling companies to comply and innovate towards sustainability.
3. Are sustainable electronics more expensive?
Initially, some sustainable electronics might have a higher price, but they often offer long-term cost savings through energy efficiency and durability.
4. How important is the repairability of electronics for sustainability?
Repairable electronics significantly contribute to sustainability by extending the lifespan of devices, reducing e-waste, and conserving resources.
5. What is the significance of a circular economy in electronics?
The circular economy minimizes waste by reusing, repairing, and recycling electronics, reducing the strain on resources and lessening environmental impact.