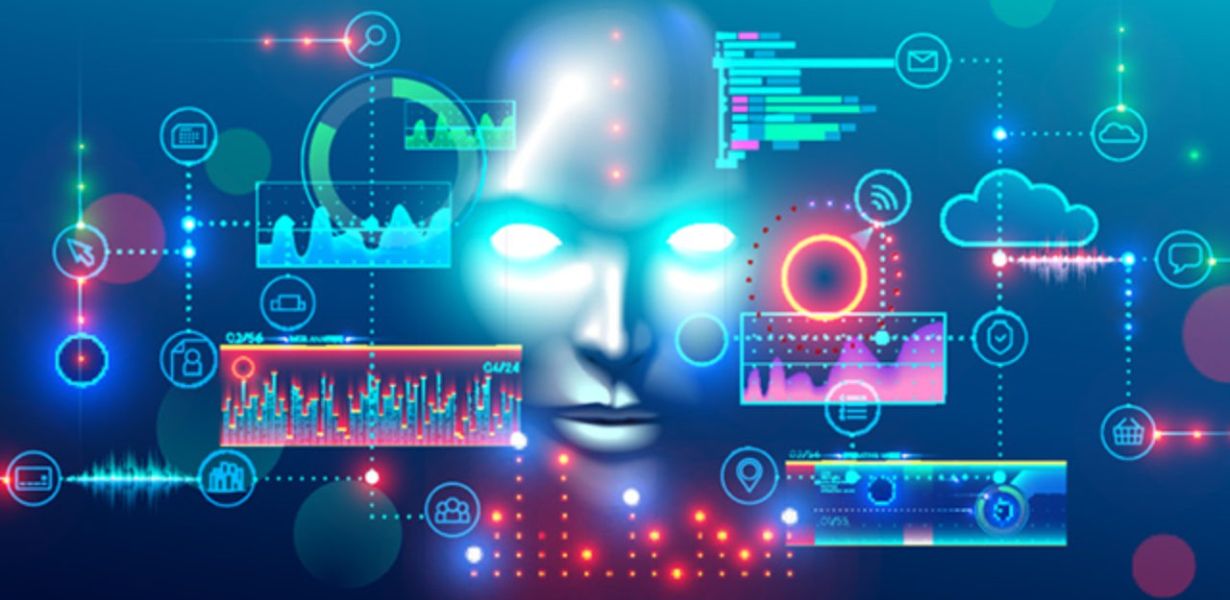
In the realm of electronics, a transformative wave is washing over us, and it goes by the name of Neuromorphic Computing. This avant-garde technology is redefining the way we approach computing, mimicking the human brain’s structure and functioning to unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency and innovation. Welcome to the future of electronics, where circuits think, learn, and adapt – a comprehensive exploration of Neuromorphic Computing.
Understanding Neuromorphic Computing
Neuromorphic Computing, the fusion of neuroscience and computer engineering, has emerged as a compelling alternative to traditional computing methods. It imitates the brain’s neural architecture and leverages its parallel processing capabilities. This innovative approach avoids the rigid constraints of conventional binary-based computing, bringing forth a realm of possibilities. Neuromorphic chips consist of millions of artificial neurons, interconnected synapses, and memory cells. They process information using spikes and respond in a more human-like fashion, breaking free from the conventional ‘0s’ and ‘1s.’ This paradigm shift in electronics is underpinned by the idea that machines can be more than mere tools; they can become cognitive entities.
The Core Principles of Neuromorphic Computing
Spike-Based Computation
Spike-based computation is the cornerstone of Neuromorphic Computing. It involves the transmission of brief electrical pulses (spikes) to relay information, much like how neurons in the brain communicate. This parallel processing ability allows for faster and more energy-efficient calculations.
Low Power Consumption
Unlike traditional CPUs and GPUs, Neuromorphic chips consume significantly less power. This power efficiency makes them ideal for portable devices, enabling longer battery life and reduced carbon footprint.
Machine Learning at its Core
Neuromorphic Computing seamlessly integrates machine learning into its architecture. This allows devices to adapt and learn from their environment, making them capable of recognizing patterns and solving complex problems autonomously.
Applications of Neuromorphic Computing
The application spectrum of Neuromorphic Computing is vast and encompasses various domains, pushing the boundaries of what electronics can achieve. Here are some key areas where Neuromorphic Computing is making a significant impact:
Robotics and Automation
Neuromorphic chips enable robots to navigate complex environments, recognize objects, and adapt to changing conditions. This technology is revolutionizing industries such as manufacturing and healthcare.
Neuromorphic Vision
In the field of neuromorphic vision, cameras equipped with Neuromorphic sensors can process visual data in real time, just like our eyes and brains. This has applications in surveillance, autonomous vehicles, and medical imaging.
Brain-Machine Interfaces
Neuromorphic Computing is at the forefront of brain-computer interfaces, allowing individuals with disabilities to control devices directly with their thoughts. It holds immense potential for enhancing human-computer interaction.
Neuromorphic Supercomputers
Supercomputers built on Neuromorphic principles are poised to tackle complex problems in areas like weather forecasting, drug discovery, and fundamental physics simulations.
Neuromorphic Computing: A Game Changer for Electronics
As we delve deeper into the possibilities of Neuromorphic Computing, it becomes evident that we are standing at the cusp of a technological revolution. This revolutionary approach to computing has the power to unlock previously unimaginable feats in electronics. From energy-efficient devices to autonomous robots and advanced medical diagnostics, the applications are boundless.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What makes Neuromorphic Computing different from traditional computing?
Neuromorphic Computing differs by emulating the brain’s neural architecture, enabling spike-based computation, and integrating machine learning at its core, leading to faster and more energy-efficient processing.
2. How is Neuromorphic Computing applied in the real world?
Neuromorphic Computing has applications in robotics, neuromorphic vision, brain-machine interfaces, and supercomputing. It’s used in fields ranging from healthcare to advanced simulations.
3. Can Neuromorphic Computing make electronics more sustainable?
Yes, Neuromorphic Computing’s low power consumption makes electronics more energy-efficient and sustainable, reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional computing.
4. Is Neuromorphic Computing safe and secure?
Neuromorphic Computing is designed with security in mind. Researchers are continuously working to ensure the safety of these systems and protect against potential vulnerabilities.
5. What does the future hold for Neuromorphic Computing?
The future of Neuromorphic Computing is promising. As research continues, we can expect more innovative applications and widespread adoption in various industries.
Final Words
In a world where electronics have become an inseparable part of our daily lives, Neuromorphic Computing stands as a beacon of innovation. It challenges the status quo and paves the way for more efficient, adaptable, and intelligent devices. As we ride this wave of transformation, the ascent of Neuromorphic Computing marks a new dawn in the realm of electronics.